82. Database index
“SQL Performance Explained” của Markus Winand là một cuốn sách hay về tối ưu hoá câu query cho SQL database. Bài viết này tổng hợp một số nội dung tôi cho là quan trọng, kèm theo link để sau này tiện tra cứu mà không cần phải đọc toàn bộ sách lại từ đầu.
1. Cấu trúc index
Link:
- [1a] https://use-the-index-luke.com/sql/anatomy/the-leaf-nodes
- [1b] https://use-the-index-luke.com/sql/anatomy/the-tree
- [1c] https://www.postgresql.org/docs/16/indexes-types.html
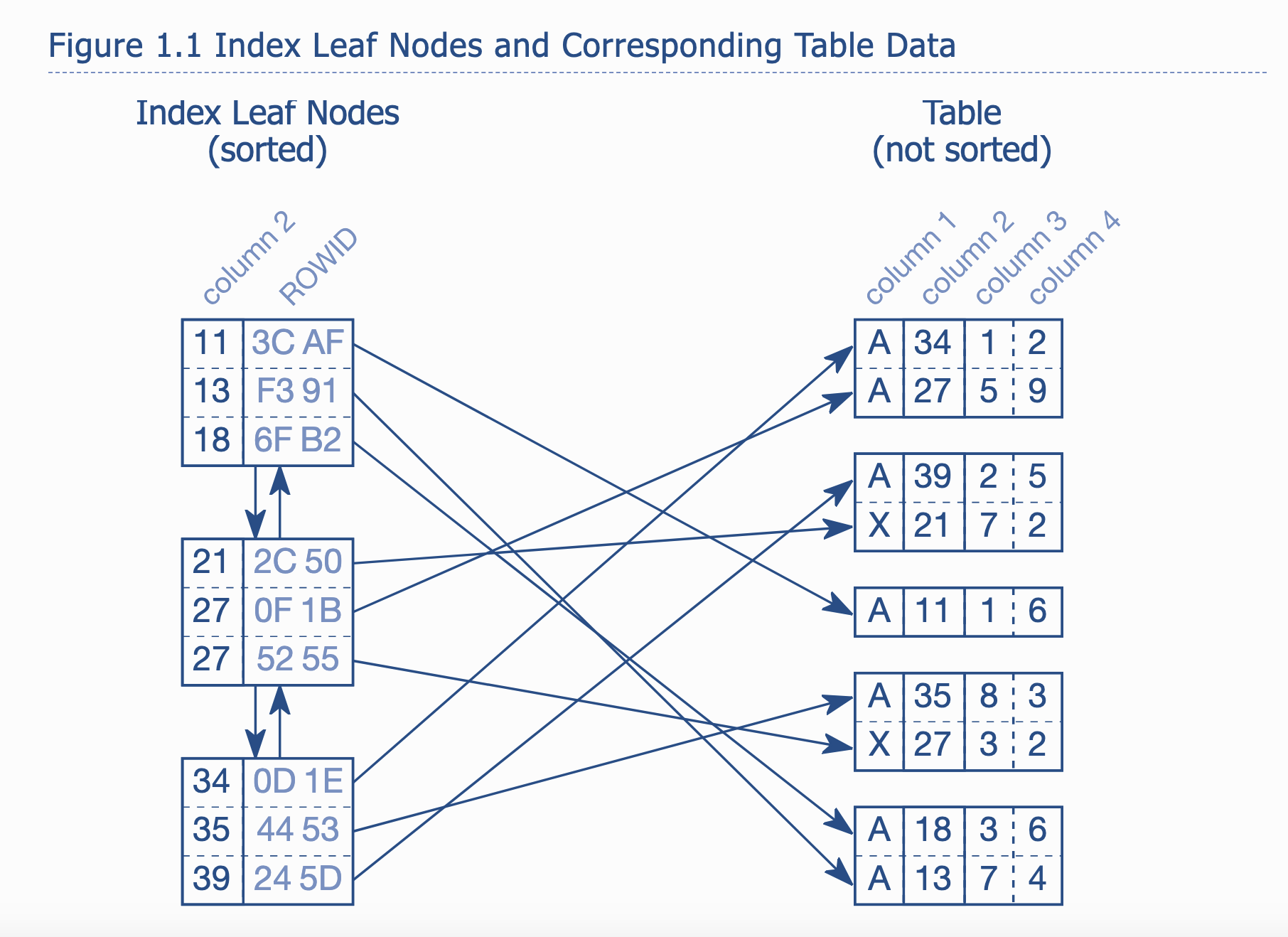
Index là 1 redundant data structure giúp câu SQL tối ưu hơn. Có nhiều thuật toán index khác nhau nhưng phổ biến nhất là B-tree. B-tree hỗ trợ các toán tử “< <= = >= >”. Có thể hỗ trợ toán tử “LIKE” trong một số trường hợp nhất định. Đọc link [1c] để hiểu rõ hơn cách database duyệt B-tree
Tại leaf-node, sẽ lưu cặp dữ liệu (value, row_id). Ở hình trên, value sẽ là giá trị của column 2 (vì ta đánh index theo column 2). row_id là physical address của row chứa giá trị column 2 tương ứng. Thông trường, index sẽ được sort theo column 2
Với Postgres, row_id sẽ gồm (block address, row offset). Khi lưu dữ liệu trên disk, dữ liệu sẽ không lưu riêng lẻ theo từng row, mà sẽ lưu theo từng block. Mỗi block có kích thước tuỳ chọn, thường là 8kb hoặc 16kb. Mỗi block có nhiều row. Row trong block không được sắp xếp. Xem hình trên,
Vì lưu dưới dạng block, nên khi cần truy suất 1 row trong block, database cần lấy toàn bộ block, và sau đó filter, loại bỏ những row không cần thiết. Do đó, nếu như câu SQL cần truy suất quá nhiều block, sẽ ảnh hưởng tới response time.
2. Các loại truy vấn dữ liệu
Để hiểu rõ hơn câu SQL được database thực thi như thế nào, ta có thể dùng lệnh EXPLAIN kèm với câu sql. Coi sách [1] để hiểu rõ hơn
Khi truy vấn dữ liệu, SQL data thường có những phương pháp phổ biến sau:
- Table full scan: quyét toàn bộ table, và thực hiện filter, bỏ những dòng không hợp lệ.
- Index Range scan: Sử dụng index, thực hiện duyệt B-tree (nếu sử dụng B-Tree), tìm ra leaf-node và dựa vào đó, tìm ra data block chứa row cần thiết. Đọc block và loại bỏ những row không cần. Phương pháp này đòi hỏi phải dùng nhiều Disk I/O. Nếu 1 lượng lớn disk cần phải đọc, đôi khi Index Range Scan sẽ chậm hơn so với Table full scan.
- Index Only Scan: Sử dụng index để tìm kiếm, tuy nhiên, nội dung tìm kiếm đều đã nằm hết ở index. Vì thế, không phải đọc disk để lấy thêm thông tin. Tham khảo thêm tại https://use-the-index-luke.com/sql/clustering/index-only-scan-covering-index
- Bitmap scan: Chỉ một số database cung cấp, trong đó có Postgres. Giả sử câu query sử dụng index_A và index_B. Bitmap scan sẽ tạo ra 1 dãy bit, sau đó đánh dấu những data block nào index_A sẽ lấy, data block nào index_B sẽ lấy. Tuỳ theo câu query mà sẽ thực hiện Bitmap And hay Bitmap OR, hay toán tử khác. Điều này giúp tối ưu việc đọc disk, không cần phải đọc 1 block nhiều lần
3. Concatenated index
Link:
- [3a] - https://www.postgresql.org/docs/16/indexes-multicolumn.html
- [3b] - https://use-the-index-luke.com/sql/where-clause/the-equals-operator/concatenated-keys
Index có thể tạo trên nhiều column. Kiểu index này gọi là compose index hay concatenated index
Giá sử index được tạo trên column (A, B). B-tree index sẽ sort theo thứ tự A và B. Do đó, index này được sử dụng nếu trong sql tìm kiến theo (A) hoặc theo (A and B). Nếu chỉ tìm kiếm theo (B), index không được sử dụng
The leftmost rule của multi-column index: key ngoài cùng bên trái phải ưu tiên toán tử = trong câu query, vì nó giúp giới hạn index range scan. Cụ thể hơn, đọc [3a]
4. Obfuscation conditions
Link
- [4a] - https://use-the-index-luke.com/sql/where-clause/obfuscation
- [4b] - https://use-the-index-luke.com/sql/where-clause/functions/case-insensitive-search
- [4c] - https://use-the-index-luke.com/sql/where-clause/searching-for-ranges/like-performance-tuning
Obfuscation condtions là câu lệnh where không thể sử dụng index cách thích hợp
SELECT first_name, last_name, phone_number
FROM employees
WHERE UPPER(last_name) = UPPER('winand')
Ví dụ, sử nếu đánh index theo last_name, nhưng câu query lại sử dụng UPPER(last_name) thì index không thể sử dụng trong thời hợp này, vì giá trị B-tree lưu là last_name, chứ không phải UPPER(last_name). Tương tự với các hàm chuyển đổi date_time, to_char, ….
Với toán tử LIKE, index chỉ có thể sử dụng cho những ký tự trước %. Xem link [4c] để rõ hơn
5. Join
“Joining is particularly sensitive to disk seek latencies because it combines scattered data fragments. Proper indexing is again the best solution to reduce response times.”[1]
“There is, however, one thing that is common to all join algorithms: they process only two tables at a time. A SQL query with more tables requires multiple steps: first building an intermediate result set by joining two tables, then joining the result with the next table and so forth.”[1]
Join order không ảnh hưởng tới kết quả cuối cùng, tuy nhiên, nó ảnh hưởng tới performance. Do đó, optimizer sẽ đánh giá tất cả các join order và chọn ra join order tốt nhất. Nếu join n bảng, sẽ có n! cách join [1].
Có ít nhất 3 phương pháp join khác nhau: Nested Loop, Hash join và Merge join. SQL optimizer sẽ quyết định chọn phương pháp join nào cho phù hợp.
Nested Loop
Link: https://use-the-index-luke.com/sql/join/nested-loops-join-n1-problem
“The nested loops join is the most fundamental join algorithm. It works like using two nested queries: the outer or driving query to fetch the results from one table and a second query for each row from the driving query to fetch the corresponding data from the other table.”
Khi sử dụng @OneToOne, @OneToMany annotation, Hibernate sử dụng Nested Loop. Vấn đề này còn được gọi là N+1 queries problem.
Nhược điểm của phương pháp này là phải thực thi nhiều câu lệnh SQL nhỏ, riêng biệt. Dẫn đến overhead network communication ==> chậm
Hash join
“It loads the candidate records from one side of the join into a hash table that can be probed very quickly for each row from the other side of the join.” [1]
- Hash joins do not need indexes on the join predicates. They use the hash table instead.
- A hash join uses indexes only if the index supports the independent predicates.
- Reduce the hash table size to improve performance; either horizontally (less rows) or vertically (less columns).
- Hash joins cannot perform joins that have range conditions in the join predicates (theta joins).
6. Sorting
Sorting rất tốn resource. Vấn đề chính yếu là database phải đọc toàn bộ result, sau đó mới thực hiện sort.
Database có thể tận dụng index để tránh explicit sort.
SELECT sale_date, product_id, quantity
FROM sales
WHERE sale_date = TRUNC(sysdate) - INTERVAL '1' DAY
ORDER BY sale_date, product_id
Nếu index (sale_date ASC, product_id ASC) tồn tại, database không cần thực hiện explicit sort mà dùng thẳng index. Nếu order by sale_date DESC, product_id DESC, database vẫn có thể dùng index cũ, vì index có thể quyét theo 2 chiều khác nhau. Tuy nhiên, nếu order by sale_date ASC, product_id DESC, không thể tận dụng index
7. Group by
Link: https://use-the-index-luke.com/sql/sorting-grouping/indexed-group-by
GroupAggregate Aggregates a presorted set according to the group by clause. This operation does not buffer large amounts of data (pipelined). This operation uses index
HashAggregateH Uses a temporary hash table to group records. The HashAggregate operation does not require a presorted data set, instead it uses large amounts of memory to materialize the intermediate result (not pipelined). The output is not ordered in any meaningful way.
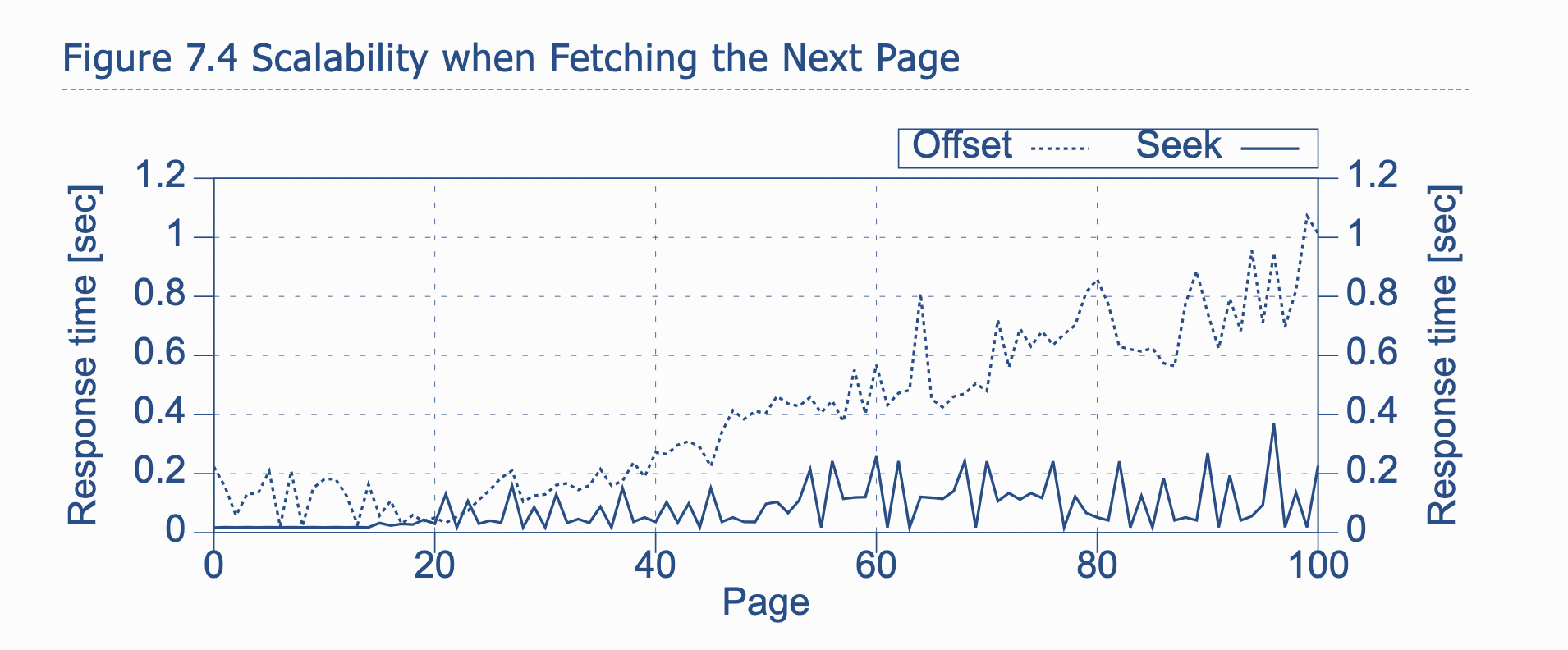
8. Partial results: Limit and seeking approach
Link:
- [8a] - https://use-the-index-luke.com/sql/partial-results/fetch-next-page
“There are two different methods to meet this challenge:
- Firstly the offset method, which numbers the rows from the beginning and uses a filter on this row number to discard the rows before the requested page.
- The second method, which I call the seek method, searches the last entry of the previous page and fetches only the following rows.” [1]
Phương pháp dùng offset, nếu muốn get page 1000, nó phải sort và thực hiện duyệt từ đầu, loại bỏ 999 page và trả về kết quả ở page 1000. Lý do là vì B-tree index, ta không có cách nào thực hiện random access tới vị trí bất kỳ như array